This module implements a halfedge mesh data structure and its associated geometry.
A halfedge mesh stores mesh elements such as vertices, edges and faces as well as
their connectivity information. The latter is particulary important in geometry
processing, as algorithms often exploit local connectivity of mesh elements. At
the cost of slightly higher memory consumption compared to other data structures,
a halfedge mesh enables quick access of mesh elements. For example, it is possible to
enumerate the vertices and edges contained in and faces adjacent to any single face
in a mesh. Similar enumerations are also possible for any vertex or edge in a mesh.
Additionally, its possible to perform global traversals that enumerate over all mesh
vertices, edges and faces in an unspecified but fixed order.
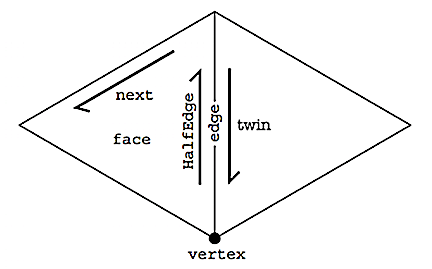
The diagram above illustrates how connectivity information is stored locally in a
halfedge mesh. The key idea is to split a edge into two directed halfedges. Each
halfedge stores a reference to the vertex at its base, the edge it lies on, the
face adjacent to it, the next halfedge in counter clockwise order, and the opposite
(or twin) halfedge. Each vertex, edge and face of a mesh in turn stores a reference
to one of the halfedges (outgoing in the case of a vertex) its incident on.